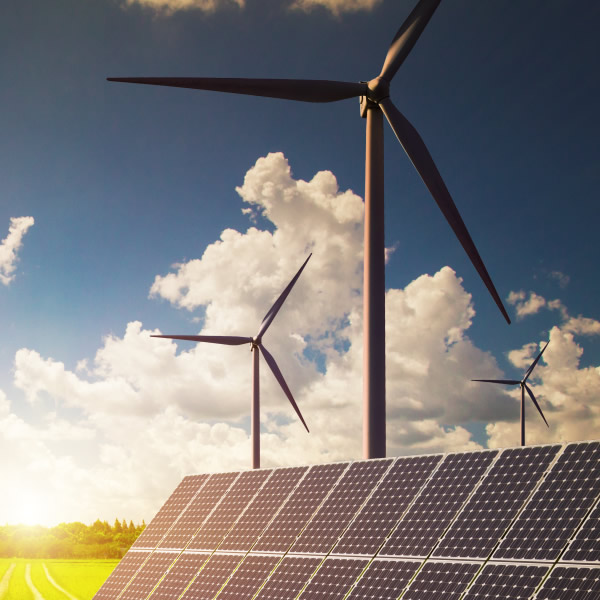

New energy generally refers to renewable energy developed and utilized on the basis of new technologies, including solar energy, biomass energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, wave energy, ocean current energy, tidal energy, as well as thermal cycles between the ocean surface and deep layers; In addition, there are hydrogen energy, biogas, alcohol, methanol, etc.
Generally speaking, conventional energy refers to energy that is technically mature and has been widely utilized, while new energy usually refers to energy that has not yet been widely utilized and is actively researched and developed. Therefore, coal, oil, natural gas, and large and medium-sized hydropower are all considered conventional energy sources, while solar energy, wind energy, modern biomass energy, geothermal energy, ocean energy, and hydrogen energy are considered new energy sources. With the advancement of technology and the establishment of sustainable development concepts, industrial and domestic organic waste, which was previously regarded as garbage, has been re recognized and deeply researched and developed as a material for energy resource utilization. Therefore, the resource utilization of waste can also be seen as a form of new energy technology.
The energy resources that have recently been developed and utilized by humans and require further research and development are called new energy. Compared to conventional energy, new energy has different contents in different historical periods and technological levels. In today's society, new energy usually refers to solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, hydrogen energy, etc.
It can be classified into: solar energy, wind energy, biomass energy, hydrogen energy, geothermal energy, ocean energy, small hydropower, chemical energy (such as ether based fuels), nuclear energy, etc.


 Tel:
Tel:
 Fax:
Fax:
 Address:
Address:
 Mobile:
Mobile:
 Address:
Address: